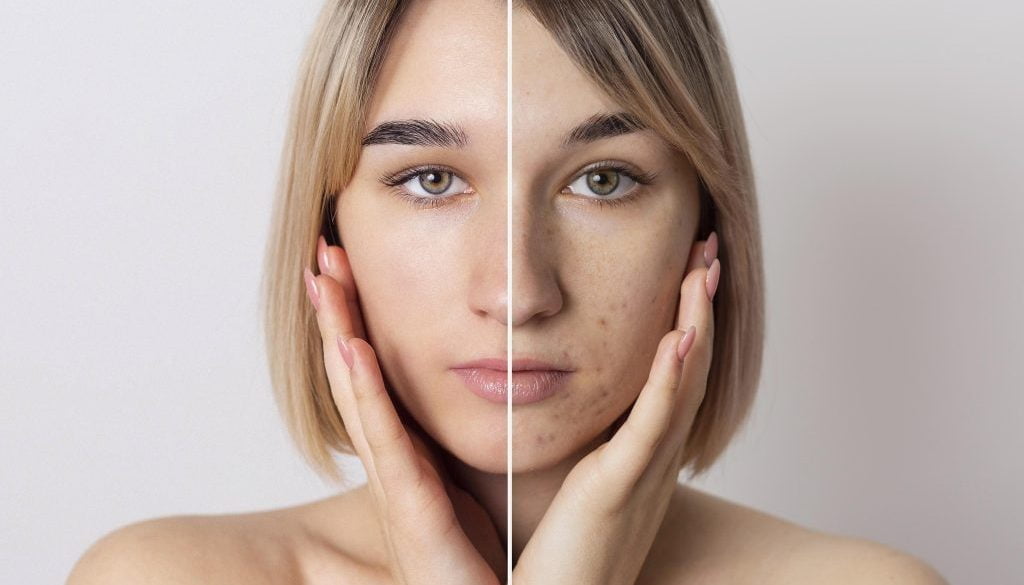
Blackheads – Definition, Formation, and Prevalence
As a skin care professional, it is crucial to understand and convey accurate information about common skin issues, such as blackheads. Blackheads, medically known as open comedones, are prevalent in skin and affect a significant portion of the population at various stages of life. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of blackheads, detailing their definition, the process of their formation, reasons for their widespread occurrence and how to remove blackheads.
Key Points (TLDR)
Definition of Blackheads
Blackheads are a type of non-inflammatory acne lesion. They appear as small, dark spots on the skin, primarily on the face, particularly the nose, chin, and forehead. The dark appearance is not due to dirt but results from the oxidation of sebum and dead skin cells exposed to air.
Formation Process
- Sebum Production: The skin’s sebaceous glands produce sebum, a natural oil that helps to keep the skin moisturized and protected. In certain circumstances, these glands produce an excess amount of sebum.
- Dead Skin Cells: The skin continually sheds dead cells as a part of its natural renewal process. Sometimes, these cells accumulate on the skin’s surface.
- Pore Blockage: When excess sebum mixes with dead skin cells, it can lead to a blockage of the hair follicles (pores).
- Oxidation: The top of the plugged follicle remains open and exposed to air, leading to the oxidation of the mixture, which turns it black, forming a blackhead.
Factors Contributing to Blackhead Formation
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations, particularly during puberty, menstruation, pregnancy, and menopause, can increase sebum production.
- Genetics: A predisposition to acne and blackheads can be inherited.
- Cosmetic Products: Certain makeup and skincare products can clog pores, especially if they are not non-comedogenic.
- Environmental Factors: Pollution and humidity can contribute to the clogging of pores.
- Lifestyle Factors: Diet, stress, and poor skincare habits can also play a role in the development of blackheads.
Prevalence
Blackheads are a common skin issue across various age groups, not limited to adolescents. They are particularly prevalent in people with oily skin types. While they are a cosmetic concern for many, blackheads can also be a precursor to more severe forms of acne if not managed properly.
Understanding the nature of blackheads is crucial for effective treatment and prevention. Recognizing the factors that contribute to their formation can help in adopting appropriate skincare routines and lifestyle adjustments to minimize their occurrence. For persistent or severe cases, consultation with a dermatologist is recommended to explore more advanced treatment options.
Contributing Factors to the Formation of Blackheads
Blackheads, a common form of acne, arise from a complex interaction of physiological factors and external influences. Understanding these factors is crucial for both skincare professionals and individuals seeking effective prevention and treatment strategies. This article delves into the primary contributors to the development of blackheads, including excessive sebum production, accumulation of dead skin cells, hormonal changes, lifestyle influences, and ways how to remove blackheads.
Excessive Sebum Production
- Sebaceous Gland Activity: The skin’s sebaceous glands produce sebum, an oily substance that helps to moisturize and protect the skin. However, overactive sebaceous glands can produce more sebum than necessary, leading to oily skin, which is a prime environment for blackhead formation.
- Genetic Factors: Genetic predisposition can influence sebum production levels. Individuals with a family history of oily skin or acne are more likely to experience excessive sebum production.
- Hormonal Influence: Hormones, especially androgens, can increase sebum production. This is why blackheads are prevalent during puberty, menstrual cycles, pregnancy, and sometimes with the use of certain contraceptives.
Accumulation of Dead Skin Cells
- Skin Cell Turnover: The skin constantly generates new cells and sheds old ones. Disruptions in this process can lead to the accumulation of dead skin cells on the skin’s surface.
- Pore Blockage: When excess sebum mixes with these accumulated dead skin cells, it can lead to clogged pores, the initial stage in blackhead formation.
- Inadequate Exfoliation: A lack of proper exfoliation can exacerbate the accumulation of dead skin cells. Regular gentle exfoliation can help in preventing this buildup.
Hormonal Changes
- Puberty: The surge in hormones during puberty typically increases sebum production, making adolescents particularly prone to blackheads.
- Menstrual Cycle and Pregnancy: Fluctuating hormone levels during these periods can also affect sebum production and skin texture.
- Stress: Stress can influence hormone levels, particularly cortisol, which can indirectly contribute to sebum overproduction.
Lifestyle Factors
- Diet: Certain dietary choices, such as high consumption of dairy products and foods with a high glycemic index, may exacerbate acne and blackheads in some individuals.
- Skincare and Cosmetic Products: Using heavy or comedogenic skincare and cosmetic products can clog pores. Non-comedogenic products are recommended for those prone to blackheads.
- Hygiene Practices: Inadequate skin cleansing can lead to the build-up of oils and dead skin cells. Over-washing or using harsh cleansers can also aggravate the skin and increase oil production.
- Environmental Factors: High humidity and pollution can contribute to pore clogging and subsequent blackhead formation.
The formation of blackheads is influenced by a combination of internal factors like sebum production and hormonal changes, and external factors such as lifestyle and environmental conditions. An understanding of these factors is essential for effective prevention and treatment. Tailoring skincare routines to address these specific contributors can significantly reduce the occurrence of blackheads. In cases where self-care measures are insufficient, seeking advice from a dermatologist or skincare professional is advisable for more targeted treatments.
Differences Between Blackheads and Other Types of Acne: Understanding Blackheads, Whiteheads and Cystic Acne
Acne is a diverse and complex skin condition that manifests in various forms, each with its unique characteristics and causes. Among these, blackheads, whiteheads, and cystic acne are some of the most common types. Understanding the differences between these forms of acne is crucial for effective treatment and management. This article will focus on delineating the distinctive features of blackheads, whiteheads, and cystic acne.
Blackheads (Open Comedones)
- Appearance: Blackheads are small, dark lesions that appear on the skin due to the oxidation of melanin. The dark color is not dirt but oxidized sebum and skin debris.
- Formation: They form when a pore is partially blocked by a combination of sebum and dead skin cells. The top of the pore remains open, exposing the blockage to air, leading to oxidation.
- Texture: The surface of a blackhead is typically slightly raised and feels rough due to the open pore.
Whiteheads (Closed Comedones)
- Appearance: Whiteheads are small, flesh-colored or white bumps. They are formed by the same combination of sebum and dead skin cells as blackheads but differ in one crucial aspect.
- Formation: In whiteheads, the pore is completely closed off, trapping the sebum and skin cells beneath the skin’s surface, preventing oxidation and thus retaining a white color.
- Texture: They often feel smoother than blackheads and are slightly raised from the skin.
Cystic Acne
- Appearance: Cystic acne is characterized by large, red, and painful bumps deep under the skin. These are more severe than typical blackheads or whiteheads.
- Formation: It occurs when an infection goes deep into the skin, creating a red, tender bump that’s full of pus. It’s the result of a combination of bacteria, oil, and dry skin cells getting trapped in your pores.
- Texture and Sensation: These lesions are often painful and can feel hard or fluid-filled. They are more likely to cause scarring due to their depth and severity.
Distinguishing Factors
- Depth of Lesion: Blackheads and whiteheads are more superficial compared to the deeper, more inflamed cystic acne.
- Pore Status: The open nature of blackheads’ pores differentiates them from the closed pores of whiteheads.
- Severity and Pain: Cystic acne is generally more severe and painful than both blackheads and whiteheads.
- Risk of Scarring: Cystic acne carries a higher risk of scarring compared to blackheads and whiteheads.
Understanding the differences between blackheads, whiteheads, and cystic acne is essential for accurate diagnosis, effective treatment and determining the right way how to remove blackheads. Blackheads and whiteheads, while aesthetically bothersome, are typically less severe and can often be managed with over-the-counter treatments and proper skincare. In contrast, cystic acne, due to its severity and potential for scarring, often requires professional medical treatment. Recognizing these distinctions allows individuals and skincare professionals to take a more targeted approach to acne treatment and prevention.
Prevention Methods for Blackheads: Skincare Hygiene, Product Selection, and Lifestyle Changes
Preventing blackheads involves a multifaceted approach that combines good skincare practices, careful selection of skin products, and mindful lifestyle choices. This article provides practical advice on how to prevent the formation of blackheads, focusing on these key areas.
Skincare Hygiene
- Regular Cleansing: Gently cleanse your skin twice a day using a mild cleanser. This helps remove excess oil and dead skin cells that can clog pores.
- Exfoliation: Incorporate exfoliation into your routine 1-2 times a week. Exfoliating helps remove dead skin cells from the surface of your skin. Use products with salicylic acid or alpha-hydroxy acids for chemical exfoliation, or a gentle scrub for physical exfoliation.
- Non-Comedogenic Products: Choose skincare and makeup products labeled as ‘non-comedogenic’, which means they are formulated not to clog pores.
- Avoid Over-Washing: Over-washing can strip the skin of its natural oils, leading the skin to produce more oil, which can contribute to blackhead formation.
- Hands Off: Avoid touching your face with your hands, as this can transfer oils and dirt to your skin.
Product Selection for Skin Care
- Oil-Free Moisturizers: Use oil-free moisturizers to keep the skin hydrated without adding extra oil.
- Retinoids: Consider products containing retinoids, which help in cell turnover and prevent clogging of pores.
- Clay Masks: Use clay masks periodically as they can help to absorb excess oil and draw out impurities from the pores.
- Sunscreen: Regular use of sunscreen can prevent the skin from producing excess oil, which is a natural defense mechanism against sun exposure.
Dietary and Lifestyle Changes
- Balanced Diet: Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Some studies suggest reducing dairy and high glycemic index foods may help with acne.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to help flush out toxins and maintain healthy skin hydration.
- Stress Management: Stress can trigger or worsen acne, so incorporate stress-reduction techniques such as yoga, meditation, or regular exercise into your routine.
- Avoid Smoking: Smoking can worsen blackheads and overall skin health by reducing blood flow and contributing to clogged pores.
- Regular Exercise: Exercise increases blood circulation, which helps nourish skin cells and keep them vital. Just be sure to cleanse your skin after sweating.
Preventing blackheads is achievable through a combination of proper skincare, the right product choices, and healthy lifestyle habits. Regular cleansing and exfoliation, using non-comedogenic products, managing diet and stress, and avoiding smoking are all effective strategies. While these measures can significantly reduce the likelihood of blackhead formation, individuals with persistent issues should consult a dermatologist for personalized advice, treatment options and and determining the right way how to remove blackheads.
Treatments for Blackheads: From Over-the-Counter Products to Professional Dermatological Procedures
Effective management of blackheads involves a range of treatment options, from readily available over-the-counter (OTC) products to more specialized dermatological procedures. This article explores various treatments for blackheads, including the use of specific active ingredients and the role of vacuum devices.
Over-the-Counter Products
- Salicylic Acid: Salicylic acid is a beta-hydroxy acid that works by exfoliating the skin and clearing clogged pores. It’s effective in treating blackheads and is available in various forms, such as cleansers, toners, and spot treatments.
- Benzoyl Peroxide: Known for its antibacterial properties, benzoyl peroxide can help prevent the buildup of bacteria that exacerbates blackheads. It’s available in concentrations ranging from 2.5% to 10%.
- Retinoids: Over-the-counter retinoids like adapalene are effective in promoting cell turnover and preventing the clogging of pores. Continuous use can lead to significant improvements in skin texture and the reduction of blackheads.
- Charcoal and Clay Masks: These masks can absorb excess oil and impurities from the skin, making them beneficial for people with oily skin prone to blackheads.
Professional Treatments
- Chemical Peels: Dermatologists may recommend chemical peels that use stronger acids to deeply exfoliate the skin and clear clogged pores.
- Manual Extraction: Professional extraction by a dermatologist or a licensed esthetician is a safe way to remove blackheads without damaging the skin.
- Microdermabrasion: This procedure involves a device that gently exfoliates the skin’s surface, removing the dead skin cells that contribute to blackhead formation.
- Laser and Light Therapy: Certain types of laser and light therapies can help reduce oil production and improve the overall texture of the skin.
Vacuum Extraction for Blackheads
- Vacuum Devices: These devices use suction to extract blackheads from the pores. While effective, it’s important to use them with caution to avoid skin damage.
- Professional vs. At-Home Devices: Professional vacuum extraction is generally safer and more effective than at-home devices. Dermatologists can adjust the suction level and duration to suit individual skin types and conditions.
- Precautions: Overuse of vacuum devices can lead to skin irritation, redness, and in some cases, bruising. It’s crucial to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and consult a professional when in doubt.
A multi-pronged approach is often the most effective strategy for treating blackheads. Over-the-counter products containing active ingredients like salicylic acid, benzoyl peroxide, and retinoids can be highly effective for mild to moderate blackheads. For persistent or severe cases, professional treatments such as chemical peels, manual extractions, and vacuum extraction can offer more dramatic results. It’s essential to tailor the treatment to the individual’s skin type and severity of the condition, and in some cases, consulting a dermatologist for a personalized treatment plan is advisable.
Blackhead Remover Vacuum
How to Remove Blackheads Naturally and with Home Remedies
Alongside clinical treatments and over-the-counter products, many individuals turn to home remedies and natural methods to manage blackheads. These approaches can be effective, particularly for those seeking gentler, more holistic skincare options. This article explores popular home remedies and natural methods for reducing blackheads.
Steam Treatment
- Method: Steaming the face can help to open up pores, making it easier to remove blackheads. Simply fill a bowl with hot water, lean over it, and cover your head with a towel to trap the steam. Do this for about 10 minutes.
- Benefits: This method helps to soften the skin and open up the pores, making it a great preparatory step before other treatments.
Exfoliation with Natural Scrubs
- Sugar Scrub: Mix sugar with a carrier oil (like coconut or olive oil) to create a natural exfoliating scrub. Gently massage the mixture onto your face in circular motions and rinse.
- Oatmeal Scrub: Oatmeal is known for its soothing properties. Combine ground oatmeal with honey and lemon juice for a gentle exfoliating scrub.
- Coffee Scrub: Ground coffee can be mixed with a small amount of water or oil to create a scrub that exfoliates and stimulates the skin.
Clay Masks
- Bentonite Clay: Bentonite clay is effective in absorbing excess oil and drawing out impurities from the pores. Mix the clay with water or apple cider vinegar to form a paste, apply it to the face, and rinse off after it dries.
- Green Clay: Similar to bentonite, green clay can be used to make a purifying facial mask.
Honey and Cinnamon Mask
- Preparation: Mix raw honey with cinnamon to form a paste. Both ingredients have natural antibacterial properties and can help to clear out pores.
- Application: Apply the mask to the face, leave it on for about 10-15 minutes, and then rinse off.
Lemon Juice
- Use: Lemon juice, rich in citric acid, acts as a natural astringent to help remove excess oil.
- Caution: Lemon juice can be drying and may irritate sensitive skin, so it should be used sparingly and diluted with water.
Tea Tree Oil
- Application: Dilute tea tree oil with a carrier oil and apply it to the affected areas. Tea tree oil has antimicrobial properties that can help clear up blackheads.
- Note: Always dilute essential oils before applying them to the skin to prevent irritation.
Dietary Considerations
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of water can help maintain the skin’s hydration and overall health.
- Balanced Diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can support skin health.
Home remedies and natural methods can be effective for reducing blackheads, especially for those with mild conditions or sensitive skin. While these methods are generally safe, it’s important to pay attention to how your skin reacts and discontinue any treatment that causes irritation or discomfort. For persistent or severe blackhead issues, consulting a dermatologist is recommended.
Common Questions and Myths About Blackheads: Addressing FAQs and Dispelling Misconceptions
Blackheads are a common skin concern, often surrounded by myths and misconceptions. This article aims to address frequently asked questions and debunk common myths about blackheads and their treatment, providing accurate information for better skin care understanding and practices.
FAQs About Blackheads
- What Causes Blackheads?
- Blackheads are caused by the clogging of pores with a mixture of sebum and dead skin cells. Factors like hormonal changes, excessive oil production, and improper skincare can contribute to their formation.
- Are Blackheads a Sign of Poor Hygiene?
- Not necessarily. While proper skin cleansing is important, blackheads are more closely related to the body’s natural oil production and hormonal fluctuations than to hygiene alone.
- Can Squeezing Blackheads Make Them Go Away?
- Squeezing blackheads can cause skin irritation and potentially lead to scarring or infection. It’s best to use proper extraction methods or treatments.
- Do Blackheads Eventually Go Away on Their Own?
- Some blackheads can clear up on their own over time, but others might persist and require treatment to be effectively removed.
- Can Diet Affect Blackheads?
- While the link between diet and blackheads is not entirely clear, a healthy diet can contribute to overall skin health. Some people may find that certain foods exacerbate their skin issues.
Common Myths About Blackheads
- Myth: Blackheads Are Dirt Stuck in Pores
- Reality: Blackheads are not caused by dirt. They are open comedones where the sebum and dead skin cells oxidize and turn black upon exposure to air.
- Myth: Only Teenagers Get Blackheads
- Reality: People of all ages can get blackheads. Hormonal changes during adolescence make teenagers more prone to them, but adults can also experience blackheads.
- Myth: More Washing Means Fewer Blackheads
- Reality: Over-washing can strip the skin of its natural oils, leading to increased oil production, which can worsen blackheads. Gentle cleansing twice a day is sufficient.
- Myth: Sun Exposure Helps Clear Blackheads
- Reality: While the sun may temporarily dry out the skin, it can cause long-term damage and lead to increased oil production. Sun exposure without protection is not a recommended treatment for blackheads.
- Myth: Toothpaste is an Effective Treatment for Blackheads
- Reality: Toothpaste can irritate the skin and is not an effective treatment for blackheads. It’s better to use products specifically formulated for acne and blackheads.
Understanding the facts about blackheads is crucial for effective prevention and treatment. It’s important to approach blackhead treatment with accurate information, avoiding common misconceptions that can lead to ineffective or harmful skin care practices. For persistent or severe cases, consulting with a dermatologist is the best course of action.
When to Visit a Dermatologist: Seeking Professional Medical Help for Blackhead Treatment
While blackheads are often manageable with over-the-counter treatments and home remedies, there are situations where professional medical advice is necessary. This article provides guidance on when it is appropriate to seek the help of a dermatologist for blackhead treatment.
Persistent or Worsening Blackheads
- Lack of Improvement: If blackheads persist despite regular use of over-the-counter treatments and proper skincare routines, it may be time to consult a dermatologist.
- Worsening Condition: If you notice an increase in the number and severity of blackheads, a dermatologist can offer more potent treatments and personalized advice.
Severe or Extensive Acne
- Large Areas Affected: When blackheads cover a large area of the skin, especially beyond the face, professional treatment may be more effective.
- Cystic Acne or Nodules: If blackheads are accompanied by more severe forms of acne, such as cysts or nodules, dermatological intervention is important to prevent scarring and further skin damage.
Ineffective Over-the-Counter Treatments
- Limited Results: If over-the-counter products fail to produce significant results, a dermatologist can prescribe stronger topical or oral medications.
- Irritation from OTC Products: If you experience adverse reactions or skin irritation from over-the-counter products, a dermatologist can recommend alternatives.
Risk of Scarring and Infection
- Scarring: If you have a history of scarring from acne or if you notice scars developing, a dermatologist can provide treatments to reduce and prevent further scarring.
- Signs of Infection: Redness, pain, or swelling around blackheads can indicate an infection, necessitating professional medical attention.
Special Cases
- Pre-Existing Skin Conditions: Individuals with pre-existing skin conditions, like eczema or rosacea, should consult a dermatologist for tailored blackhead treatments that won’t exacerbate their conditions.
- Hormonal Concerns: If you suspect your blackheads are related to hormonal issues, a dermatologist can offer treatments that address the hormonal aspect of acne.
Professional Advice on Skincare Routine
- Tailored Skincare Regimen: A dermatologist can provide a customized skincare routine that is most effective for your skin type and concerns.
- Guidance on Product Selection: Dermatologists can recommend products that work well with your skin and are effective against blackheads.
Visiting a dermatologist for blackhead treatment is advisable when over-the-counter solutions are ineffective, in cases of severe or extensive acne, when there’s a risk of scarring, or if you have special skin concerns. Dermatologists offer a range of treatments and personalized advice, ensuring that the approach to managing blackheads is both effective and safe for your skin type and condition.
Insights from Acne Case Studies: Focus on Blackhead Treatment
Acne, a common skin condition, manifests in various forms, including the prevalent issue of blackheads. Drawing insights from case studies at Face Reality Acne Clinic*, this article explores the diverse presentations of acne and the approaches to treating blackheads within these contexts.
Inflamed Acne and Blackheads
- Characteristics: Inflamed acne is identified by redness, sensitivity, and the presence of pimples, pustules, whiteheads, and blackheads. In some cases, cysts may also be present.
- Treatment Approaches: The treatment for this type involves addressing both inflammation and clogged pores. This may include the use of topical treatments like benzoyl peroxide or salicylic acid, which help reduce inflammation and exfoliate the skin, thereby clearing blackheads.
Noninflamed Acne with Blackheads
- Characteristics: Noninflamed acne presents a dull, sluggish appearance with bumps, blackheads, and fewer pimples or pustules compared to inflamed acne. The skin is typically not sensitive or reactive.
- Treatment Approaches: For noninflamed acne with blackheads, exfoliation is key. Treatments may focus on unclogging pores through gentle exfoliation and the use of non-comedogenic products to prevent further blockage.
Acne with Hyperpigmentation
- Characteristics: This type includes a dull appearance with hyperpigmentation spots where acne has occurred, along with a mix of inflamed and noninflamed acne, often accompanied by excessive oil and congestion.
- Treatment Approaches: The focus here is on managing active acne while addressing hyperpigmentation. This might involve a combination of exfoliating agents and skin-brightening ingredients, along with treatments for blackheads.
Rosacea and Blackheads
- Characteristics: Rosacea is characterized by facial flushing, redness, and in some cases, papules and pustules. It can be aggravated by factors like alcohol, spicy foods, temperature changes, or exercise.
- Treatment Approaches: For individuals with rosacea and blackheads, treatment must be gentle to avoid aggravating the rosacea. This might involve mild exfoliating products and soothing agents.
Back Acne (Bacne) and Blackheads
- Characteristics: Back acne can include inflamed or noninflamed lesions, often leaving dark spots where acne was present.
- Treatment Approaches: Treatment for back acne with blackheads may require stronger formulations than facial acne due to the thicker skin on the back. Exfoliation and targeted treatments to reduce oil production and clear pores are common strategies.
The case studies from Face Reality Acne Clinic highlight the varied nature of acne and the necessity of tailored treatments, especially when dealing with blackheads. Understanding the specific type of acne and its characteristics is crucial in determining the most effective treatment approach. For individuals struggling with blackheads, whether as part of inflamed or noninflamed acne, a combination of exfoliation, appropriate skincare products, and in some cases, professional treatment, is essential for effective management and clear skin.
Key Insights and Motivational Message for Those Struggling with Blackheads
Battling blackheads can be a challenging journey, but understanding and applying the right strategies can lead to successful outcomes. This article summarizes key points from previous discussions on blackheads, aiming to provide motivation and guidance for those seeking clearer skin.
Summary of Key Points
- Understanding Blackheads: Blackheads, or open comedones, are a form of non-inflammatory acne caused by the clogging of pores with a mix of sebum and dead skin cells.
- Contributing Factors: Factors like hormonal changes, excessive sebum production, accumulation of dead skin cells, and lifestyle habits contribute to the formation of blackheads.
- Distinguishing Blackheads from Other Acne Types: Blackheads differ from whiteheads (closed comedones) and more severe forms like cystic acne in appearance, formation, and severity.
- Prevention Strategies: Regular cleansing, proper exfoliation, using non-comedogenic products, and adopting a healthy lifestyle can help prevent blackheads.
- Effective Treatments: Over-the-counter products with salicylic acid, benzoyl peroxide, or retinoids can be effective. For persistent cases, professional treatments like chemical peels, manual extractions, or vacuum extraction may be necessary.
- Home Remedies and Natural Methods: Natural methods, including steam treatments, natural scrubs, and clay masks, can be beneficial for managing blackheads.
- When to Consult a Dermatologist: Seek professional help if blackheads persist despite home treatment, if there is severe or widespread acne, or if there is a risk of scarring.
- Personal Experiences and Case Studies: Individual experiences with blackhead treatment vary, underscoring the importance of a personalized approach.
If you’re struggling with blackheads, remember that you’re not alone. This common skin issue affects many, but with the right knowledge and approach, it can be managed effectively. Your journey to clearer skin may have ups and downs, and what works for one person might not work for you. It’s important to be patient and persistent. Experiment with different treatments and lifestyle changes to find what best suits your skin.
Remember, the path to better skin isn’t just about the products you use; it’s also about understanding your skin’s unique needs and nurturing it accordingly. Embrace a holistic approach that includes a balanced diet, adequate hydration, and stress management.
In cases where you feel overwhelmed, don’t hesitate to seek professional advice. Dermatologists can provide tailored treatments and valuable insights tailored to your skin’s specific needs.
Above all, be kind to yourself and your skin. Progress may be gradual, but with consistent care and the right approach, clearer, healthier skin is an achievable goal. Stay motivated, stay informed, and believe in your skin’s ability to heal and thrive.